how to find two way radio frequency
Updated 06/2021
Two Way Radio 101 - Danger , Experts Made Hither!
Ever find yourself staring at shelves of two-mode radios, or hopelessly scrolling through web folio subsequently spider web folio trying to make sense of information technology all? We've all been there. Nosotros created this article to provide insight into how radios operate allowing you improve understanding of your electric current two-mode radios. It will also help you to feel informed and empowered to brand the best purchasing conclusion for whatever future ii-mode radios, putting an end to all that endless scrolling.
We volition look at all sorts of two way radio topics:
- Frequency Bands
- Simplex, Conventional, and Trunked Two-Way Radio Systems
- Manual Types
- Narrowbanding
- FCC Licensing
- License-free radios
- LTE & Satellite Radios
- Radio Etiquette
This article will lay a solid foundation of knowledge for yous, interim equally a dandy resources to keep in your bookmark tab for hereafter utilize. We're all certified experts having read something only once, right?
Buckle upward, partner, let's get going!
Two Style Radio Frequency Bands
There are all kinds of frequencies in which dissimilar two-way radios can function.
" BUT Look! " Yous say. "I don't even know what you mean by frequencies."
Not to worry friends, let's outset with an intro into what a frequency is, and those of united states of america who are coming into this with prior experience can experience free to skip ahead.

Call up of frequencies equally waves in a pool of h2o. Nosotros outset with a still pool, in which there would be a frequency of 0 considering the water is static.

At present imagine we requite in to temptation and do a cannonball into the puddle. Think nigh all the waves we will create equally nosotros disturb the water's surface. Look at one spot in the pool and counthow many waves laissez passer past in v seconds. The numberof waves yous count in that time is the frequency .

Encounter, Frequency is the number of waves that pass a stock-still signal in a unit of time. Using the image in a higher place, we can see a more uniform depiction of what the term frequency is describing. The unit of measurement of time being used in that image is ane second. We can run into that the frequency represented here is 2 Hertz or 2 Hz. Hertz is the unit used to measure frequency. A Hertz refers to the amount of fourth dimension it takes a wave to complete 1 bicycle, represented above.

The effigy to a higher place gives a visual of frequencies at different wavelengths placed on top of each other. Wavelengths are defined as the distance between corresponding points of two sequent waves; refer to the epitome below. The wavelength determines how many cycles are possible during a unit of fourth dimension. The longer the wavelength the lower the frequency and therefore the shorter the wavelength the college the frequency, depicted moving downwards the lines.

Now, the frequencies two-way radios use are much higher than our 2Hz instance. Nosotros will need to call back in terms of Kilo- (1,000's) and Mega- (1,000,000's) Hertz for the earth of two-mode radios.
Permit'south say we are using a VHF, Very High Frequency, two-way radio organization which operates in a 138 -174 Megahertz, or MHz, frequency band (or range). This means our system is sending out radio waves with a frequency of 138,000,000 – 174,000,000 Hertz per second. Crazy fast, and can y'all believe this is 1 of the lower ranges for frequency bands that 2-style radios utilize?
Modernistic two-way radios operate using frequency bands from 134MHz up to around 900Mhz. The two-fashion radio systems we will look at today will be using frequency bands labeled:
- Very High Frequency (VHF) ~ 138-174 MHz
- Ultra High Frequency (UHF) ~ 400-512 MHz
- 800MHz ~ 806-824 MHz & 850-869 MHz
- 900MHz ~ 896-901 & 935-940 MHz
Why the variety of bands operating across such a large range of frequencies? The elementary respond is lower and higher frequencies allow radios to exist more specialized for dissimilar applications.
Recollect how lower frequencies have longer wavelengths? This allows radios using lower frequencies to be more suitable for outdoor employ over greater distances considering the longer wavelengths will bend with the horizon. The lower frequencies are corking for farmers, hunters, hikers, park rangers, etc., only they come at a toll of not performing likewise in more urban settings. Longer wavelengths practice non accept much penetrating power, assuasive them to bounce off the atmosphere and bend around the horizon, simply this means they won't become through dense materials like those in walls.
A radio wave with a college frequency can more effectively get through walls and is very useful in urban settings, only the shorter wavelengths make it less useful over large distances. This is because the shorter wavelengths will penetrate straight through the atmosphere and continue in a straight fashion.

A nifty existent-world example of this is when we consider AM vs FM radio. AM radio stations can exist broadcasted clearly over hundreds of miles while we start to hear static from FM radio stations after getting about 30 – twoscore miles away from the station. This is because AM radio is broadcast over a frequency ring of 0.525 – 1.705 MHz, with longer wavelengths able to better bend with the horizon (figure higher up), while FM uses a broadcast range from 88 – 108 MHz. FM radio uses the college frequencies to navigate the more urban environments it is usually circulate from more smoothly, merely won't keep a clear bespeak for as far.
Very Loftier Frequency (VHF) Radios
VHF radios operate inside the frequency band of 138 – 174 MHz
Why employ VHF Radios?
Radios that use this frequency ring work best in open, flat terrain. Equally you lot might think, radios with lower frequencies provide you with a meliorate ability to communicate over long distances. Retrieve back to the AM radio case. The longer wavelengths of a lower frequency radio allow your point to bend over the horizon to reach your team fellow member miles and miles away.
Who uses VHF Radios?
VHF radios are used at large by the recreational outdoor customs and by public condom commissions, especially in rural counties.
I'm a surveyor looking to stay in contact with HQ while I am out conducting research well-nigh the mural. A VHF radio is ideal for me because it allows me to cover neat distances while knowing I volition be able to stay in contact with my colleagues for both data communication and safety.
Are there drawbacks to VHF Radios?
While VHF two-manner radios are corking for rural use, dense foliage in thick forests and dramatic landscapes can notwithstanding cause interference, or static, with your signal. Those long wavelengths just don't like it when things get in their way. A clear line of sight is a big cistron for the success of your VHF 2-way radio system.
As well, if you lot are in the eye of downtown Chicago attempting to reach your friend who is working in a high-rise, you may experience some interference with your signal. This static is caused by the lack of signal strength as it attempts to penetrate through the many buildings. Information technology could also be due to point interference by other two-way radio communications since the longer wavelengths are more easily affected.
Ultra High Frequency (UHF) Radios
UHF radios utilize a frequency band of 400 – 512 MHz
This frequency band is by far the most popular pick amongst two-manner radio users.
Why use UHF Radios?
People will generally get with UHF radios for indoor use or for when in that location are obstacles between users. Dissimilar radios employing VHF, those that employ the UHF frequency band are perfect for utilise in a downtown setting like Chicago. The shorter wavelengths requite these radios the power to become your message to your team member with ease. The concrete, glass, and other signal sources comport no friction match to the penetrating ability of a UHF radio organisation.
Who uses UHF Radios?
UHF radios are ideal for professionals working in areas with densely packed buildings. Think about your security details in buildings or special events, hotel staff, and taxi services navigating the urban surround.
You are a House Manager for a production playing in New York City. You lot need to have open up advice with your assistants and other staff to assure the convenience and safety of all audition members. You would be all-time served past a UHF radio system as it can navigate the environment you have with ease.
Are in that location drawbacks to UHF Radios?
As with VHF radios, the drawbacks of two-way radios using the UHF spectrum really come into play when you try to use it for a scenario it isn't designed for. The distances involved in outdoor recreation play to the weaknesses of a UHF system. Unless, of grade, yous are out surveying rainforests or mountainous terrain and demand the strength of the UHF'southward shorter wavelengths to go through the awning or rock formations.
Go along the wavelengths examples in heed. The shorter wavelengths for the higher frequency UHF system will shoot right through the atmosphere, given plenty ability, meaning it will not bend around the horizon. Remember back to the image of the AM/FM/Idiot box waves simply to a higher place, with the higher frequency, FM, signals standing through that atmosphere while the AM bespeak bounced dorsum down to the surface.
Absolutely your typical UHF ii-fashion radio system won't take the power to actually send a signal straight through the atmosphere. Instead it'll only misemploy. Those examples still provide a expert visual to keep in heed even though indicate dissipation most ofttimes occurs when a bespeak is being reflected over too many surfaces without the power to continue.
800 & 900 MHz Two-Way Radios
These systems utilize frequency bands of 800 MHz - 806 – 824 MHz & 851 – 869 MHz and 900 MHz - 896-901 & 935-940 MHz
Who uses 800 & 900 MHz Radios?
These frequency bands are primarily for use by public safety services similar police officers, firefighters, and emergency medical technicians, but in that location are some commercial wireless carriers and private radio systems utilizing them as well.
For case, manufacturing, utility, land transportation, and petrochemical companies all brand use of the 900 MHz frequency ring.
Many of these organizations utilize a trunked radio arrangement considering of their many devices and interdependence needs. More details almost trunked radio systems to come up, but the picture below volition give you lot a simple visual of a trunked system.
Why employ 800 & 900 MHz Radios?
A trunked arrangement with such strong frequencies pairs the groovy penetration power of high frequencies with the control of having control centers navigate the advice paths. Coming in handy for the primarily urban areas these are most utilized.
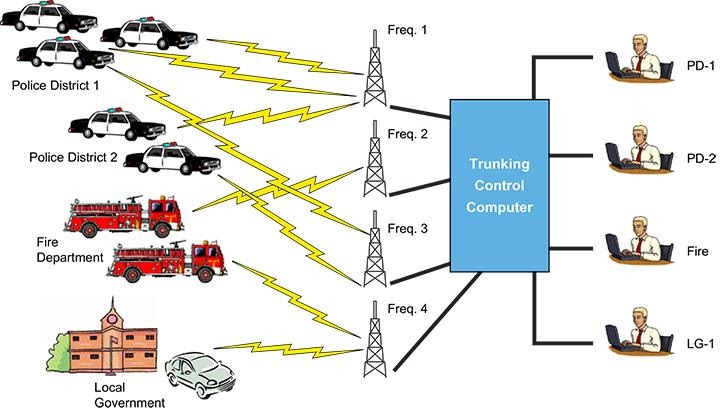
Are there drawbacks to 800 & 900 MHz radios?
Since the frequency is so high, these systems are very dependent on strategically placed antennas to allow for the large distances needed covering to be communicated over effectively. It is the same problem we face with UHF bands, with more ability involved.
About 2-mode radios operating in these bands require license agreements. Though ane license-free selection is the DTR700 past Motorola because of its low power usage, at 1-Watt. It is great for retail stores or small businesses in a tightly packed environment.
We have a keen article going into more detail virtually the benefits of different frequency bands here . The article also goes a fleck more in-depth about why ane should choose a VHF or a UHF two-way radio system.
Simplex, Conventional & Trunked Two-Fashion Radio Systems
Your ii-way radio system can use a few different methods of transmitting signals based on its programming. Nosotros will look at each in order of growing complexity. This section can exist a bit dense, so frequent h2o breaks are recommended.
Simplex Radio to Radio Systems
Simplex systems use a single channel to transmit and receive information. These systems are strictly radio to radio using no repeaters for a signal boost.
Analog Simplex
- Radio to radio using analog transmissions.
- Does not use high powered repeaters, or in-betwixt, radio systems.
- Any analog or digital radios support this.
Digital Simplex
- Radio to radio using digital transmissions.
- Does not use high powered repeaters, or in-between, radio systems.
- Whatsoever digital radios support this.
- All components (radios and repeaters) must use the aforementioned digital technology to operate.
- DMR - for Motorola
- NXDN - for Icom and Kenwood.
Conventional Systems
Conventional systems will utilize repeaters for boosting your signal. These systems have channels bachelor for the user to select, as well every bit instant aqueduct access.
Analog Conventional
- Radio to Repeater to Radio using analog transmissions.
- Uses a high powered repeater to boost the signal.
- Any analog dealer programmable radio (non-FRS) can exist programmed to back up this transmission method.
Digital Conventional
- Radio to Repeater to Radio using Digital transmissions.
- Uses a high powered repeater to heave the signal.
- Whatever digital radios can exist programmed to support this.
IP Site Connect
- Radio to Repeater to Radio using digital transmissions.
- This technology can link multiple repeaters together via the cyberspace (IP), which creates a system of repeaters all transmitting the transmissions at the same time. This creates a larger network of "conventional" repeaters for companies that want to connect multiple locations with common communications.
- You can connect upwards to 15 repeaters at 15 unlike sites using this technology.
- The Motorola XPR 3000 series, XPR 7000 series, SL 3500e, SL 7000 serial, and XPR 5000 series mobiles back up this applied science
Trunked Systems
Trunked systems are when your communication is beingness transmitted from your radio to a control station which then chooses where your transmission will end up and on which frequency. These systems utilize a "pool" of frequencies that the control station can send communications over.
Capacity Plus Trunking
- Radio to Repeater to Radio using digital transmissions.
- This engineering science creates "pools" of available channels where users are dynamically allocated based on what's currently available. It is bachelor in single-site operation or linked-capacity-plus, which acts like IP site connect.
- This engineering science is recommended for big plants or users with like needs.
- You tin can add up to 120 repeaters at 15 unlike sites supporting up to i,600 radios/site or 24,000 radios full.
- The Motorola XPR 3000 serial, XPR 7000 series, SL 3500e, SL 7000 series, and XPR 5000 series mobiles all support this technology
Capacity Max Trunking
- Radio to Repeater to Radio using digital transmissions.
- This technology as well creates "pools" of available channels where users are dynamically allocated based on what's currently available. Dissimilar from capacity plus trunking, in these systems, if all bachelor channels are full, users will be added to a queue.
- This engineering is recommended for extremely large operations. You can add together up to 5,250 repeaters at 250 different sites supporting upward to 3,000 radios/site or ninety,000 radios total. This is the most complex level of two manner radio systems bachelor.
- The Motorola XPR 7000 series, SL 7000 series, and XPR 5000 series support this technology
Below, is an example of a trunked communication system. You lot can encounter how a diverseness of users are able to communicate. None of them are directly transmitting to each other (radio-to-radio); all communications are going through the antenna to the command computer and so redirected out into the field based on the need.

A couple other things to continue in mind:
- None of the methods discussed are ring-specific, pregnant you can plan nigh whatever frequency band to utilise either simplex, conventional, or trunked transmission methods.
- All repeater systems TX (transmit) and RX (receive) on unlike frequencies. Unremarkably, for the UHF band this offset is 5 MHz, but for VHF it tin be more or less than that.
Two-Way Radio Manual Types
For over a century analog signals ruled the radio world, but the advancement of technology is once again changing things and radio is not allowed to the digitization of the modern earth. Even though most businesses and users still utilize analog systems today, the shift to digital systems is coming. A large driving forcefulness of this is the analog technology has hit a ceiling with innovations and people are nevertheless finding new needs in this ever-changing world.
Here yous will see a brief breakup of analog and digital systems, if you would like to know more well-nigh why making the motion to digital could be beneficial, visit our commodity Analog 5. Digital – 7 Cardinal Differences to learn more.
Analog
Analog transmissions have been available for businesses since 1933 and used by the armed forces for 20 years before that. Equally the name suggests, analog systems go along your voice as a wave while it travels to the receiver.
Most analog radios today apply frequency modulation, or FM, producing a continuous wave with the voice indicate. Advancements like FM have greatly reduced the cost and fabricated analog systems very user friendly over its long tenure.
Benefits of Analog Radios
- Due to the longer time analog has been effectually, in that location are a bully many accessories and add-ons available to analog systems. However, expect for this to change in the near future as many manufacturers are discontinuing their analog product altogether.
- The "drain off zone". While digital radios have ~25% better range (re analog vs digital article), once they hit max range the transmissions just end. Much like an Hard disk radio in a motorcar. Meanwhile, analog radios tin peter off slowly, which results in static but may eke out a little more range under specific situations.
- Analog systems use the natural vocalization since the signal is kept as a wave betwixt receivers, something many users adopt
Disadvantages of Analog Radios
Digital
The newcomer on the scene, digital systems are still coming of age only are rapidly gaining basis on analog's stronghold in the radio community. This is in big office because digital systems began at the elevation of analog engineering science and provide the potential for innovations far beyond analog capabilities.
Benefits of Digital Radios
- Innovation – The main benefit to using a digital arrangement is how it enables you to seamlessly enhance your systems every bit new innovations striking the market
- Digitization of vox – considering a digital radio immediately translates your vocalization into just figurer language ( 0's and one'south ), you can better utilise your maximum range of the radio as well as meliorate vox clarity between users by minimizing external background noise
- Conversation chapters – digital systems offer more than paths of simultaneous communication as well as the power to add unit of measurement ID's and enhanced text message into a single channel
- Battery Life – the digital arrangement offers ~ 40% more than battery life than analog radios
- Backwards compatibility – Nigh digital systems come standard with the ability to communicate with your established analog devices by using select analog channels.
Disadvantages of Digital Radios
- Cost – currently digital radios do toll the consumer more, merely as with analog radios, you should look for this toll to driblet dramatically as more innovations come into the market
- Learning curve – due to the software and enhanced functionality, digital systems can come up with a learning period that some get-go-time users may find off-putting
- Quality of Sound - some users that have been using analog radios for a while might not like the "tinny" nature of digital transmissions. Although this can be offset on some high-end radios by adjusting the audio profiles.
Digital Schools of thought
With airwave congestion from the ever-growing two-fashion radio consumer market, the FCC and other legislative bodies have had to put regulations in place to protect the time to come growth of the industry every bit well as the security of communications.
The rising of digital radio systems has provided pathways for companies to lessen the amount of bandwidth needed per aqueduct. In essence, the digital system can split the amount of bandwidth used in half through various technological advancements.
DMR – Digital Mobile Radio
Motorola utilizes this technology as their digital standard
This standard was created by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), that uses a technology called Time Partition Multiple Access (TDMA).
TDMA takes your total bandwidth, 12.5KHz, and splits it up into two alternating fourth dimension slots with each slot interim every bit a separate advice pathway.
This engineering science allows for fewer frequencies needed for the licensee
NXDN – Adjacent Generation Digital Narrowband
This engineering was developed by the companies ICOM and Kenwood. It utilizes Frequency Partition Multiple Access (FDMA).
FDMA doubles your bandwidth capability like TDMA when compared to an analog system only does so by separating the conversations by frequency instead of using time slots.
You must recollect that the two standards, DMR and NXDN, will not communicate with each other. Pregnant, if you lot have a fleet of Motorola radios using DMR to communicate, you cannot add together ICOM or Kenwood radios and expect them to integrate into your system seamlessly. In that instance yous would need to decide whether to add together more Motorola radios, or swap out your entire fleet, to come across your needs.
Narrowbanding
Before 2013, everybody was using systems that operated with a bandwidth of 25KHz. This was far too large when factoring in the growing number of users vying for space in the radio spectrum, every day.
The congestion caused by the large bandwidth is why the FCC mandated that all existing and time to come licensees implement equipment able to operate on bandwidths of 12.5KHz by Jan. i, 2013, with the eventual goal of getting the bandwidth size down to 6.25KHz.
It'southward this goal of reaching the 6.25KHz bandwidth that drove the innovations of TDMA and FDMA technologies because you are unable to transmit the vox equally a wave through such a small bandwidth. Digitization for the win!
To visualize narrowbanding, recall almost a grouping of people standing shoulder to shoulder betwixt two walls. Equally they are, there is no more space to fit anyone else. Now anybody turns to face one direction, creating space, or slots, between each person for someone else to occupy. This is a basic description of what the move to narrowbanding accomplishes.

The effigy above shows how many more channels become bachelor by the move to smaller and smaller bandwidths. At vi.25KHz, we have quadrupled the number of channels available for the radio community at every frequency.
FCC Licensing
The Federal Communications Commission, or FCC, is responsible for regulating the electromagnetic spectrum used by commercial and private users. They oversee optimizing the use of the spectrum for fair contest as the revolution in communication continues.
Many personal radio users will find they tin can operate without specific licenses granted past the FCC, but it is always good to know what is available for y'all as your needs may change.
General Licensing Info
- License agreements given out by the FCC will concluding for ten years
- You can renew your license upwards to 90 days or less of your understanding expiring, and are granted a two-year grace flow for renewal after your license expires
- Fees for licenses vary based on a number of factors. Hither are a few things that go into calculating the cost of a new or revised FCC license.
- Blazon of license applied for, such every bit:
- Coordinated, license centered on set locations. More expensive
- Itinerant, license based on large areas of usage, unremarkably nationwide. Cheaper than coordinated licenses, just more apt to interference from other itinerant users as the frequency pool is pocket-size and shared via all itinerant licensees
- Ability Output, higher power mostly = higher costs
- Manual Blazon, analog or digital
- Advanced trunking systems
- Area of impact (mainly concerns coordinated licenses)
- An example of a college license fee would exist if you are at a high elevation in an urban area and want to put in a high powered repeater system. Your radio coverage would travel very far, which would need to be accounted for.
- Exist enlightened that some license agreements accept an historic period requirement of 18 years or older
If you'd like to learn more specifics near the process of obtaining an FCC license forGMRS orLMR radios, clickhere. In our FCC licensing article we go over reasons why you would need one blazon of license over the other, we explain the process of acquiring each license type, and get over someFAQ'southward most licensing.
Another great resource for your licensing questions is fcc.gov under the mobility sectionalization of the Wireless Telecommunication Bureau. In that location you'll find detailed breakdowns of all their licensing scenarios.
Admittedly, the FCC's site is pretty dense then I'd recommend trying out ourFCC Licensingarticle or calling one of our Motorola Primary Certified radio consultants at (888) 733-7681 who would exist happy to respond whatever questions, first before getting bogged down on the FCC'south official site..
With that in mind, let's have a moment for a quick overview of some licensing scenarios put forth by the FCC.
Family Radio Systems (FRS) vs Full general Mobile Radio Service (GMRS) vs Land Mobile Radio (LMR)
Family Radio Systems (FRS)
As defined by the FCC , the Family Radio Service (FRS) is a private, two-way, brusk-distance voice and data communications service for facilitating family unit and group activities.
Nigh FRS radio devices are the type yous notice on the shelves of stores like Walmart, Best Buy, and sporting good locations . These make up the majority of the apprentice consumer market for two-fashion radios.
The FCC has designated 22 channels for FRS use within the 462 – 467 MHz range information technology shares with GMRS.
Since you lot share the modest frequency range with all FRS users, at that place's a good chance you'll find yourself in a situation hearing others conversations. If and so, exist respectful, change the channel.
Products in this category are "licensed by rule", meaning a user does not need a license so long they are operating within the rules laid out by the FCC.
One of these rules is a 2-watt power limit for devices using the FRS, if your device exceeds this limit you volition have to inquire about receiving a licensing agreement before use.
An FRS user is not permitted use of a repeater, or antenna, to farther the range of their devices.
General Mobile Radio Systems (GMRS)
The FCC defines GMRS equally a licensed radio service that uses channels betwixt 462 MHz and 467 MHz. The most mutual employ of GMRS channels is for short-altitude, two-style voice communications using hand-held radios, mobile radios, and repeater systems.
GMRS operates under the aforementioned 462 – 467 MHz frequency ring as FRS
These systems are mainly licensed out to individuals who demand to employ radio systems which exceed the 2-watt power limit put on FRS devices, simply at that place are some cases where small-scale businesses may utilize GMRS as well.
Yous must be xviii years of age to apply for a GMRS license agreement.
If you obtain a GMRS license, family members and those in your company can operate the GMRS stations and units within your license understanding regardless of age.
Your license agreement lasts for 10 years.
GMRS license agreements allow users to implement repeaters and stations to further their communication capabilities.
Land Mobile Radio (LMR)
Note: This is the class of ii mode radio sold by RadioDepot
LMR services are generally much higher quality and more complex than its GMRS and FRS counterparts.Public country mobile radio systems are to be used exclusively by p ublic safety organizations (i.due east. police, fire, and ambulance services), and use designated special frequencies reserved for the public safe sector by the FCC. Private land mobile radio systems are designed for private commercial use and are utilized past businesses ranging from loftier-rise hotels land surveying companies.
Devices in the LMR sector are all superior quality, rugged past design, and have high output power wattages. Making them ideal for the industrial and business sector.
LMR has been granted several frequency bands within which they tin operate:
- thirty-50 MHz (Low VHF Ring)
- 150-172 MHz (Loftier VHF Band)
- 450-470 MHz (UHF Ring)
- 800 & 900 MHz bands (UHF)
As with GMRS, you lot are required to obtain a license from the FCC to legally operate your LMR device in any of the above mentioned frequency bands.
You volition need to apply for your LMR FCC frequency license by making use of a frequency coordinator so both yours and everyone else'south communication networks will all piece of work smoothly.
- When buying a radio from us, we will assistance you in this process. Nosotros take relationships with frequency coordinators to make everything become smoothly
Your LMR Frequency License will be valid for ten years
When applying for license, you will have to declare the roughquantity of devices,use of repeaters and any other network altering devices you plan to use. While this may seem tedious, it volition let your frequencies to be laid out the best for you lot and allow for any device you lot take programmed to the frequencies to be used freely.
For more than details on the differences between the FRS, GMRS, and LMR sectors take a look at FRS vs GMRS vs LMR.
Itinerant vs Coordinated Licenses
Itinerant Licenses
These licenses are for people who need their license agreements to travel with them. Call up near an contained contractor working on multiple chore sites throughout counties or even dissimilar states. Itinerant licenses provide you lot the ability of non having to reapply for license agreements for each location you work in.
The FCC has gear up aside a list of frequencies for use by all afoot licensees. This does mean there is a higher risk of advice interference due to the book of users over the same frequencies.
Coordinated Licenses
The FCC requires Part 90 licensing for a divers band of radio products called Public Land Mobile Radio Services (PLMR). Types of radio devices typically requiring Part ninety certification are public prophylactic radios (EMT, burn down, police, etc.), paging devices, commercial radio systems, and radio location devices.
Coordinated licenses are for individuals or organizations looking to operate within the FCC's business/industrial puddle of frequencies under Part xc certification. Such entities are required to obtain a radio station license for their frequencies.
A frequency coordinator, private organizations certified past the FCC, is needed to recommend the most appropriate frequencies for your needs.
Many people and companies choose to use radio licensing agencies to simplify this process. For example, Radio Depot can help you secure a license without ever having to communicate directly with the FCC or a coordinator.
Applicants for these licenses must show proof of frequency coordination to be considered. This process is to ensure the efficiency of the PLMR spectrum for the benefit of the public.
License-Free 2-Fashion Radios
Many of you volition find you won't have any demand for products that crave FCC licensing. Hither is a list of some radios that can operate license-gratis, along with some details of each, giving you lot a sense of what'southward available without having to utilise for a license agreement. For more data on whatever of the products listed, click the link attached.
DTR700 by Motorola
- Utilize digital transmission
- Platonic for schools, hospitality services, retail, and churches
- Has 50 channels in the 900MHz frequency band
- Max power output = one-Watt
NX-P500 by Kenwood
PKT-23 by Kenwood
TK-3230DX by Kenwood
VL50 by Motorola
Each of these models is bang-up for small-scale apply. They have their own unique benefits better suiting them for individual cases. If interested, exist sure to research their specifics or inquire one of our certified consultants to assist guide you lot.
As always, we desire you to be the most prepared when considering buying whatever product.
LTE & Satellite Two-Way Radios
LTE and satellite radio technologies make up a significantly smaller portion of the radio markets today than Land Mobile Radios (LMR), but each has unique characteristics making them expert to have some noesis about.
LTE Radios
LTE, standing for Long Term Development, is a trademark owned by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) and is an open standard for digital cellular applied science. This technology has been developed for very high chapters data transfer with very depression latency over networks. Your modern cell telephone makes utilize of the LTE network every solar day.
The biggest deviation in LTE radios over regular LMR systems we take talked about is how they transmit data.
LTE uses data transmission. These radios convert your voice into information packets which are then re-assembled every bit audio voice on the receiving finish. This is ideal for the market that is transitioning to smaller and smaller bandwidth usage (6.25KHz).
The impressive data performance LTE systems offer could hateful they become more standard in even the most future, but presently they have some serious drawbacks keeping them from popularity. The image below will give you an idea of how an LTE system transmits your data. Notice how everything is beingness relayed through the cell tower.

LTE Radio Drawbacks
- The most meaning pitfall of LTE radio systems today is due to the incredibly modest cell size they employ for transmitting your data.
- The small information cells require significantly more than towers for transmitting than your typical LMR systems. This will inherently create very loftier costs.
- Your information operation as well greatly decreases as you motility further away from a tower.
- The LTE coverage is bandwidth sensitive relying on the network to load at any time. Significant your transmission could exist greatly afflicted near your coverage purlieus, and in heavy traffic scenarios, could fail altogether
Satellite Radios
Satellite radios are dandy for applications where your communications need to be covered over vast distances, in remote locations, or in extreme terrain.
This technology utilizes transmission via satellite link to connect radio users, making information technology possible for communication in instances where traditional LMR systems will fall short.

The above effigy gives a simple analogy of how satellite communication is done. Two antennas facing the satellite can relay information to each other.
At that place are a few dissimilar types of satellites that you can employ for satellite radio communication.
- Geosynchronous Orbit (GEO)
- High Globe orbit, ~ 22,236 miles or 35,786 km, with speed matching the earth's rotational velocity so it appears to be at a stock-still indicate in the sky.
- Provide unrivaled communications coverage with only three or iv needed to be able to encompass almost the entire earth
- Center Earth Orbit (MEO)
- Orbit altitude ~ 1,243 miles (2,000 km) up to the high earth orbit
- Travel at their ain speeds requiring automatic tracking by dishes or having to look for the next available satellite to pass past
- Depression Earth Orbit (LEO)
- Orbit altitude ~ 112 miles (180 km) up to the medium earth orbit
- Also travel at their own speeds requiring automated tracking by dishes or having to wait for the next bachelor satellite to pass by.
There are likewise a few dissimilar methods of communicating with the orbiting satellites available.
- The U.Southward. based company Iridium offers a system that incorporates brief-case sized portable battery-powered terminals which you can plug into for satellite link. Y'all simply need to point the receiver in the full general management of the satellite to obtain a link. The links these systems give are rather slow, not supporting broadband but are proficient for simple tasks like two-way communication.
- There are besides VSAT (very pocket-size aperture terminals) satellite communications systems which are ii-style basis stations set up with an antenna. These systems can point to or track a item satellite. VSATs not only can be stationary but tin can be fastened to a vehicle due to their small size and tin be disassembled and re-located quickly. These systems also support much higher data rates allowing for more complex tasks.
Drawbacks of Satellite Radios
- Satellite radio advice tin become costly very quickly, not only considering of the avant-garde instruments you must use, simply also due to the data rate pricing model for manual. With both Iridium and VSAT systems, you pay a flat rate past-the-minute or past-megabyte which can be very expensive when compared to options here on Earth.
- For satellite upwardly/downlink to piece of work your antenna must be in true line-of-site with the satellite. Many instances that can throw your connection off include being in a forest with a dense awning, at the bottom of a ravine, or on crude seas. Even accidentally knocking into your antenna can disconnect you from your satellite link.
- Another possible downside is the time it takes for your bespeak to travel the distance between the basis, the satellite, and dorsum down to Globe. This means your system will experience latencies of typically up to a half-2d for GEO'due south and but a little less for MEO and LEO'due south. That one-half-2nd doesn't sound similar too much but can mean you are not able to communicate or command remote machinery in real-fourth dimension.
- Lastly, your system is vulnerable to the single-point-of-failure in your satellite. This can be due to mechanical errors, the growing amount of droppings in orbit around the planet, or solar flares. Also, MEO and LEO satellites are vulnerable to atmospheric elevate causing eventual loss of distance.
If you find you still need data, the Tait radio academy has great articles most LTE and Satellite radios and is an all-around great resources.
Two-Style Radio Etiquette
Acquiring your radio system is only the kickoff of your radio career. There are communication techniques that will allow you to brand the virtually of your conversations over the radio. Yous don't want to spend all this money and terminate up not being able to become your point across, right?
Golden Rules of Radio Communication
- Clarity : Speak in a clear vox, normally a bit slower than normal speech. E'er speak in a normal tone, never shouting.
- Simplicity : Go along your messages simple.
- Brevity : Go along your letters precise and to the point.
- Security : Never transmit confidential information over the radio unless y'all are absolutely sure your security systems are intact. Always go on in mind radio frequencies are shared with express security lockouts, especially for analog transmissions.
Some more bones rules to know for radio transmission are:
- The accepted international radio language is English, except in some cases where you are specifically licensed to utilize another language.
- Think before y'all speak!
- Decide what y'all are going to say and who information technology is meant for
- Avoid abbreviations unless they are well understood by your grouping
- Look your turn to speak. Radio frequencies only transmit one affair at a time, if you effort to speak while some other is speaking you volition only miss that information.
- Do not answer if y'all are not certain the call is for you. Look for the appropriate call sign before yous respond
- Perform regular radio checks to ensure your system is in good status
- Make a habit of returning your receivers to their charging bases to ensure your radios battery life
- Memorize phone call signs, locations, and radio stations people y'all communicate with regularly, use.
- Look a few seconds between "handoffs" to allow for others to break into the conversation
- After pressing the PTT (button to talk) push button, wait a moment before speaking to ensure your entire message is picked up by your radio.
Below is a sample conversation putting some of these conversation standards into utilise.
Alex : Mark , this is Alex . Over .
Mark : Alex , this is Marking , Stand Past. Over .
Marking : Alex , this is Mark , Get Ahead. Over .
Alex : Marker , this is Alex , there is a car accident at mile marker 6 on Interstate 55. Over .
Mark : Alex , this is Mark , confirming the car accident at mile marker 6 on Interstate 55, emergency services will be notified. Over .
Alex : Marker , this is Alex , location confirmed, thank you for the help. Over and Out .
Notice the consistent use of each other's names as well as endmost each transmission with "over". Radio users make apply of a common language for clear communication.
- Go Ahead – Resume transmission
- Say Again – Re-transmit your message
- Stand-by – Transmission has been best-selling, simply I am unable to respond at present.
- Roger – Message received and understood.
- Affirmative – Yep (avert yup, nope, etc.)
- Negative – No
- Over – Transmission finished.
- Out – Communication is over, and the channel is available for others.
When talking over the radio yous should make use of the Standard NATO Alphabet when spelling out words over the radio to ensure your message is received properly.
| A - Alpha | B - Bravo |
| C - Charlie | D - Delta |
| E - Repeat | F - Foxtrot |
| G - Golf | H - Hotel |
| I - India | J - Juliet |
| Yard - Kilo | L - Lima |
| M - Mike | N - November |
| O - Oscar | P - Papa |
| Q - Quebec | R - Romeo |
| S - Sierra | T - Tango |
| U - Uniform | V - Victor |
| W - Whiskey | X - X-ray |
| Y - Yankee | Z - Zulu |
Conclusion
Well, it was a long journey, but we fabricated information technology! This cognition yous've got isn't simply going to greatly prepare you for all your radio needs, only likewise let you show off to your friends while you talk about Geosynchronous satellite orbits and hash out wavelengths by the pool.
Do remember, that revisiting this information will always help to in-grain it further.
For any further questions, requite us a call at (888) 733-7681 or fill out our contact u.s. class for support
Source: https://www.radiodepot.com/blogs/resources/radio-101-the-complete-two-way-radio-guide
Posted by: alleneaunded1981.blogspot.com

0 Response to "how to find two way radio frequency"
Post a Comment